i Have Rights Worksheet P.2 Answers:Embark on a journey to understand the multifaceted concept of rights and responsibilities, delving into their types, sources, protection mechanisms, and societal implications.
This comprehensive guide provides a clear understanding of the rights and responsibilities individuals possess, emphasizing the importance of balancing these elements for a harmonious society. By exploring real-world examples and engaging discussions, this resource equips readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of rights and responsibilities in today’s world.
1. Rights and Responsibilities: I Have Rights Worksheet P.2 Answers

Rights and responsibilities are fundamental concepts that govern the behavior of individuals within society. Rights are entitlements or freedoms that are inherent to every person, while responsibilities are obligations or duties that individuals have towards themselves and others.
Examples of Rights and Responsibilities
- Right to life:Responsibility to preserve one’s own life and respect the lives of others.
- Right to education:Responsibility to acquire knowledge and skills for personal and societal development.
- Right to vote:Responsibility to participate in the democratic process and make informed decisions.
Importance of Balancing Rights and Responsibilities
Striking a balance between rights and responsibilities is crucial for maintaining a just and harmonious society. When rights are prioritized over responsibilities, it can lead to excessive individualism and a lack of accountability. Conversely, when responsibilities outweigh rights, it can result in oppression and the erosion of individual freedoms.
Consequences of Violating Rights or Neglecting Responsibilities
Violating rights or neglecting responsibilities has severe consequences. Rights violations can lead to legal penalties, social stigma, and psychological harm. Neglecting responsibilities can damage relationships, undermine personal well-being, and hinder societal progress.
2. Types of Rights
Rights can be categorized into various types based on their nature and scope.
Civil Rights
Civil rights are fundamental freedoms that protect individuals from government infringement. They include the right to life, liberty, property, and due process of law.
Political Rights
Political rights empower individuals to participate in the political process. They include the right to vote, run for office, and form political parties.
Social Rights
Social rights ensure access to basic necessities and promote human well-being. They include the right to education, healthcare, and social security.
Economic Rights
Economic rights safeguard the economic interests of individuals. They include the right to work, fair wages, and decent working conditions.
Interrelationship of Rights
Different types of rights are interconnected and interdependent. For example, civil rights provide the foundation for political participation, while economic rights support social well-being.
3. Sources of Rights
Rights have evolved over time through various sources.
Historical Origins
The concept of rights can be traced back to ancient civilizations, such as Greece and Rome. The Magna Carta (1215) and the English Bill of Rights (1689) are notable historical documents that established fundamental rights and freedoms.
Constitutions, Laws, and International Treaties
Constitutions and laws codify rights and provide legal protection. International treaties, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), set out universal standards for the recognition and protection of rights.
Social Movements and Cultural Norms
Social movements and cultural norms have played a significant role in shaping and expanding rights. Movements for civil rights, women’s rights, and LGBTQ+ rights have pushed for the recognition and protection of these rights.
4. Protection of Rights
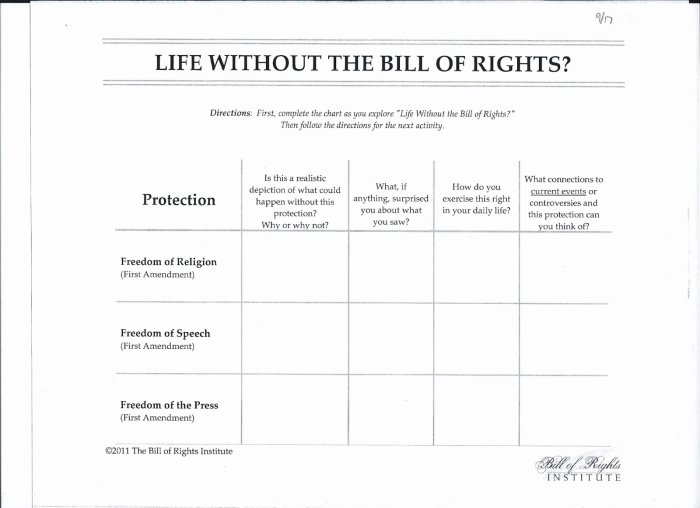
Various mechanisms exist to protect rights.
Courts
Courts adjudicate disputes and enforce rights. Individuals can seek legal remedies when their rights have been violated.
Human Rights Commissions
Human rights commissions are independent bodies that investigate human rights violations and make recommendations for redress.
Ombudsmen
Ombudsmen are impartial officials who investigate complaints against government agencies and advocate for fair treatment.
Civil Society Organizations
Civil society organizations play a crucial role in advocating for rights, monitoring their implementation, and holding governments accountable.
Challenges and Limitations, I have rights worksheet p.2 answers
Despite these mechanisms, protecting rights remains a challenge. Lack of access to justice, political interference, and cultural biases can hinder the effective enforcement of rights.
Question Bank
What are the key types of rights?
There are various types of rights, including civil rights (protecting personal freedoms), political rights (ensuring participation in governance), social rights (guaranteeing access to essential services), and economic rights (ensuring fair economic opportunities).
What are the main sources of rights?
Rights originate from various sources, including constitutions, laws, international treaties, social movements, and cultural norms.
How can rights be protected?
Mechanisms for protecting rights include courts, human rights commissions, ombudsmen, and civil society organizations.