Embark on an enlightening journey with acids and bases crossword puzzle answers, a gateway to unraveling the complexities of these fundamental chemical concepts. Delve into the definitions, properties, and applications of acids and bases, gaining a comprehensive understanding of their significance in various fields.
From the intricacies of the pH scale to the dynamics of acid-base reactions, this guide will illuminate the concepts, empowering you with a deeper comprehension of acids and bases.
Definitions and Concepts
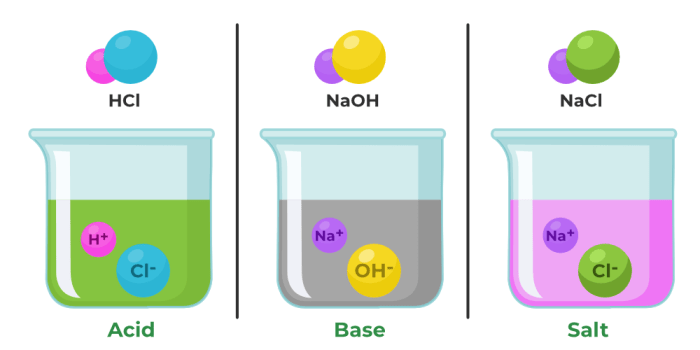
Acids and bases are two fundamental chemical concepts that describe the behavior of substances in water. Acids are substances that donate protons (H+), while bases are substances that accept protons. Acids typically have a sour taste, turn litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
Bases, on the other hand, have a bitter taste, turn litmus paper blue, and feel slippery to the touch.
Common Acids and Bases, Acids and bases crossword puzzle answers
- Acids:Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), acetic acid (CH3COOH)
- Bases:Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), ammonia (NH3)
pH Scale: Acids And Bases Crossword Puzzle Answers
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Solutions with a pH below 7 are acidic, while solutions with a pH above 7 are alkaline (basic).
The pH of a solution can be calculated using various methods, including:
- Litmus paper:A simple and inexpensive method that involves dipping a piece of litmus paper into the solution.
- pH meter:A more accurate method that uses an electrode to measure the electrical potential of the solution.
- Chemical indicators:Substances that change color depending on the pH of the solution.
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are chemical reactions that involve the transfer of protons between acids and bases. There are three main types of acid-base reactions:
- Neutralization:A reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of a salt and water.
- Hydrolysis:A reaction between an acid or a base and water that results in the formation of ions.
- Salt formation:A reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of a salt.
Acid-Base Titration
Acid-base titration is a technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. It involves adding a known volume of a standardized base or acid to a solution of the unknown substance until the solution reaches the equivalence point, where the moles of acid and base are equal.
The equivalence point can be determined using various methods, including:
- Phenolphthalein indicator:A colorless indicator that turns pink at the equivalence point.
- Methyl orange indicator:A red indicator that turns yellow at the equivalence point.
- Conductivity measurements:A method that measures the electrical conductivity of the solution.
Applications of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have a wide range of applications in various industries and sectors, including:
- Food preservation:Acids are used as preservatives to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi.
- Medicine:Acids and bases are used in the production of drugs, vitamins, and other medical products.
- Manufacturing:Acids and bases are used in the production of plastics, fertilizers, and other industrial chemicals.
- Environmental protection:Acids and bases are used to neutralize pollutants and clean up environmental spills.
FAQ Summary
What is the pH scale used for?
The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids donate hydrogen ions (H+) in water, while bases accept hydrogen ions.
What is the purpose of acid-base titration?
Acid-base titration determines the concentration of an unknown acid or base by neutralizing it with a solution of known concentration.


