Practice classification using dichotomous keys answers unveils a fascinating world of scientific inquiry and exploration. Dichotomous keys, as the title suggests, are invaluable tools that empower us to identify and classify organisms with precision and efficiency. Embark on a captivating journey as we delve into the intricacies of dichotomous keys, uncovering their applications, challenges, and advanced techniques.
Dichotomous keys, like skilled detectives, guide us through a series of carefully crafted questions, each leading us closer to the identity of an unknown specimen. They have found widespread use in diverse fields, from biology and ecology to botany and zoology, enabling scientists and researchers to make accurate identifications and advance our understanding of the natural world.
1. Introduction to Dichotomous Keys: Practice Classification Using Dichotomous Keys Answers
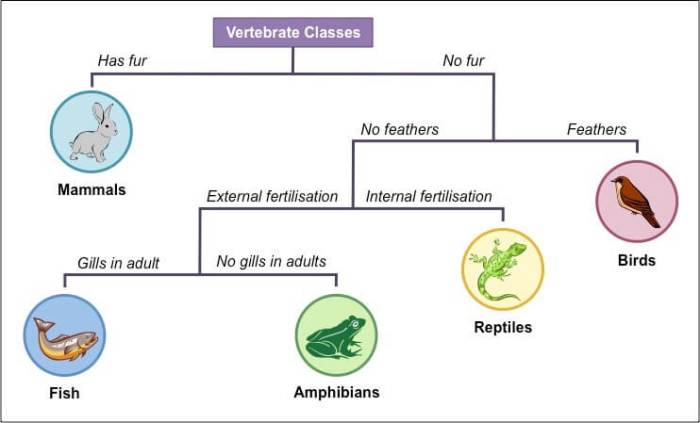
Dichotomous keys are a valuable tool for classifying organisms, minerals, and other objects based on their observable characteristics. They present a series of paired statements or questions, each with two contrasting options. By carefully selecting the option that best describes the specimen, the user is guided through a series of logical steps until they reach a final identification.
Dichotomous keys are widely used in various fields, including biology, geology, and archaeology. In biology, they are employed to identify species based on their physical attributes, behavior, or habitat. In geology, they help classify rocks and minerals based on their composition, texture, and other properties.
Archaeologists use dichotomous keys to identify artifacts and determine their cultural origin.
2. Steps in Using Dichotomous Keys
Using dichotomous keys effectively requires careful observation and logical reasoning. The following steps Artikel the process:
- Start at the beginning of the key and read the first pair of statements or questions.
- Observe the specimen and determine which option best describes it.
- Follow the arrow or number associated with the selected option to the next pair of statements or questions.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until you reach a final identification.
- Verify the identification by comparing the specimen to the description or image provided in the key.
3. Examples of Dichotomous Keys
Dichotomous keys can vary in complexity and length depending on the subject matter. Here are a few examples:
| Field | Example |
|---|---|
| Biology |
|
| Geology |
|
| Archaeology |
|
4. Challenges in Using Dichotomous Keys
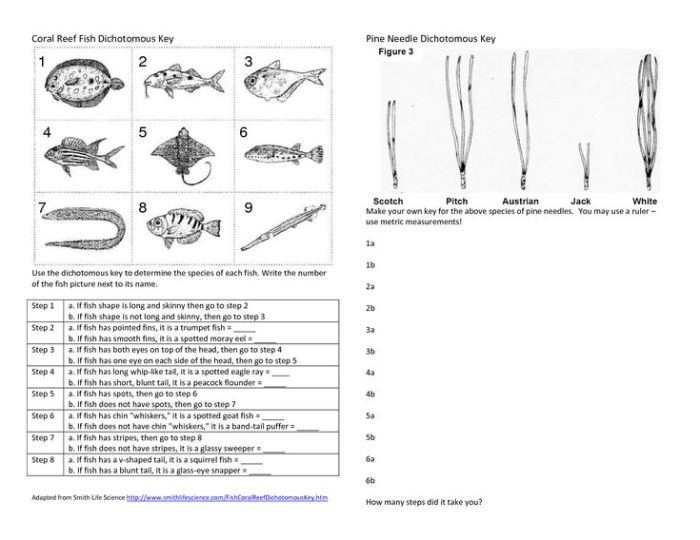
While dichotomous keys are generally straightforward to use, there are some potential challenges:
- Ambiguous characteristics:Some specimens may have characteristics that fall between the two options presented in the key, making it difficult to make a clear choice.
- Incomplete or inaccurate information:Keys may not always include all relevant characteristics or may contain errors, which can lead to incorrect identifications.
- Lack of experience:Using dichotomous keys effectively requires some level of experience and familiarity with the subject matter.
5. Applications of Dichotomous Keys
Dichotomous keys have a wide range of applications in scientific research, field identification, and other areas:
- Taxonomy:Classifying and identifying organisms, minerals, and other objects based on their characteristics.
- Field identification:Quickly and accurately identifying species in the field without the need for extensive laboratory equipment.
- Ecological studies:Determining the distribution and abundance of species in different habitats.
- Conservation:Identifying endangered or threatened species and monitoring their populations.
- Education:Teaching students about classification and identification methods.
6. Advanced Techniques in Dichotomous Key Construction
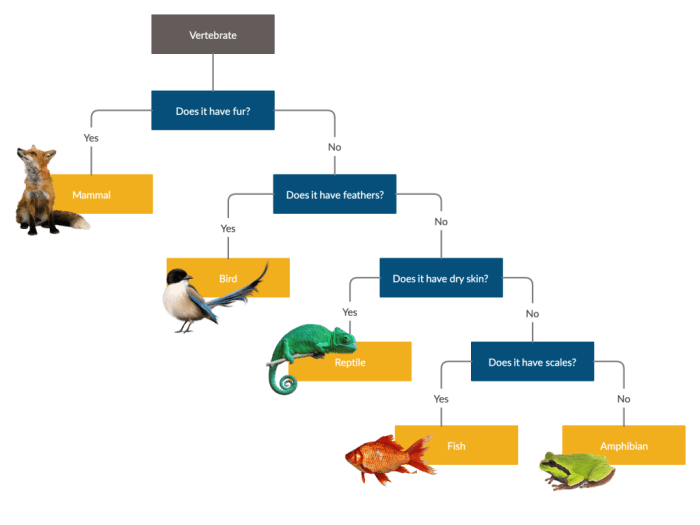
In addition to traditional dichotomous keys, there are advanced techniques for constructing more efficient and accurate keys:
- Statistical analysis:Using statistical methods to determine the most informative characteristics for distinguishing between taxa.
- Computer-aided techniques:Employing software programs to generate interactive dichotomous keys that can handle complex data sets.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary purpose of a dichotomous key?
Dichotomous keys are designed to facilitate the identification of unknown specimens by guiding users through a series of binary choices based on observable characteristics.
How can I overcome challenges when using dichotomous keys?
Careful observation, attention to detail, and a logical approach are crucial. Consulting multiple sources and seeking expert guidance can also enhance accuracy.
What are some advanced techniques used in dichotomous key construction?
Advanced techniques include statistical analysis, computer-aided identification, and the use of interactive online keys.