The National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process is a transformative framework for developing and implementing evidence-based guidelines in prehospital care. It involves key stakeholders, systematic reviews, and consensus-building to ensure the delivery of high-quality, evidence-informed care to patients in prehospital settings.
This process has been successfully implemented in various contexts, leading to improved patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare systems. By adhering to the principles of evidence-based practice, prehospital providers can make informed decisions based on the latest research and best practices.
National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process Overview
The National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process is a systematic and transparent approach to developing and implementing evidence-based guidelines for prehospital care. The process aims to improve the quality and consistency of prehospital care by ensuring that it is based on the best available evidence.
The process involves a multidisciplinary team of stakeholders, including clinicians, researchers, and policymakers. The team works together to identify and evaluate relevant evidence, develop recommendations, and implement the guidelines into practice.
The National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process has been successfully implemented in several countries, including the United States, Canada, and Australia. The process has been shown to improve the quality of prehospital care and reduce variation in practice.
Key Components of the Model Process
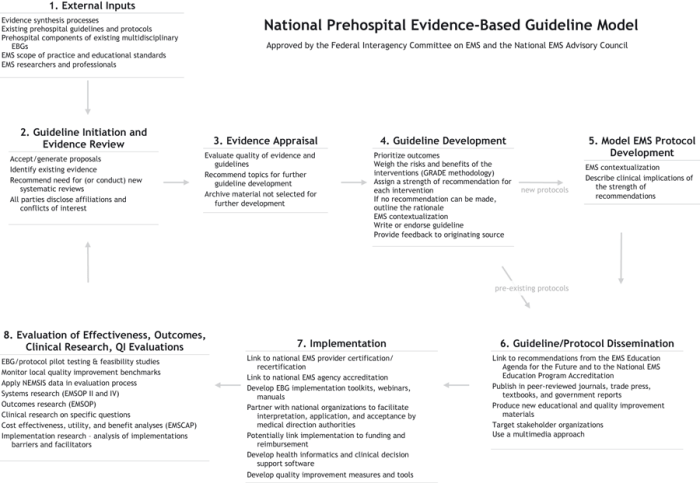
The National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process consists of several key steps:
- Identify the clinical problem or question.
- Conduct a systematic review of the evidence.
- Develop recommendations based on the evidence.
- Implement the guidelines into practice.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the guidelines.
Systematic reviews are an essential part of the evidence-based guideline development process. Systematic reviews involve a rigorous and transparent search for all relevant studies on a particular topic. The studies are then assessed for quality and the results are synthesized to provide an overall assessment of the evidence.
Stakeholder engagement is also essential to the success of the evidence-based guideline development process. Stakeholders include clinicians, researchers, policymakers, and patients. Stakeholders should be involved in all stages of the process, from identifying the clinical problem to implementing the guidelines into practice.
Challenges and Considerations
There are a number of challenges that can be faced in implementing evidence-based guidelines in prehospital care. These challenges include:
- Lack of time and resources.
- Lack of awareness of the guidelines.
- Resistance to change.
There are a number of strategies that can be used to overcome these challenges. These strategies include:
- Providing education and training on the guidelines.
- Making the guidelines easily accessible.
- Involving stakeholders in the development and implementation of the guidelines.
It is also important to consider the ethical and legal implications of implementing evidence-based guidelines. For example, it is important to ensure that the guidelines are not used to restrict access to care or to justify discriminatory practices.
Evaluation and Impact of the Model Process
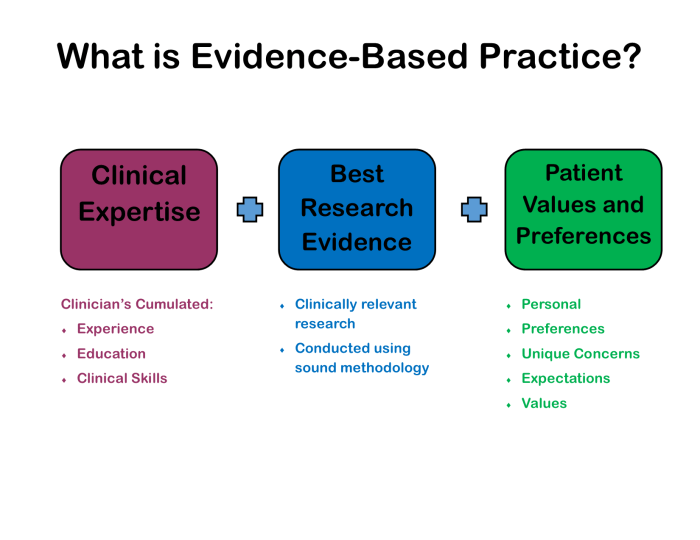
The effectiveness of evidence-based guidelines can be evaluated using a number of methods, including:
- Process evaluation: This evaluates the implementation process, such as the number of clinicians who are aware of the guidelines and the number of patients who are treated in accordance with the guidelines.
- Outcome evaluation: This evaluates the impact of the guidelines on patient outcomes, such as the number of deaths, complications, and hospitalizations.
The National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process has been shown to have a positive impact on patient outcomes and healthcare systems. For example, a study of the implementation of evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of chest pain in prehospital care found that the guidelines reduced the number of deaths and hospitalizations.
Future Directions and Innovations

There are a number of emerging trends and innovations in the development and implementation of evidence-based guidelines. These trends include:
- The use of technology to enhance the guideline development process.
- The development of patient-centered guidelines.
- The use of real-world data to evaluate the effectiveness of guidelines.
These trends are likely to continue to shape the future of evidence-based guideline development and implementation. The National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process is a valuable tool for developing and implementing evidence-based guidelines in prehospital care. The process is systematic, transparent, and stakeholder-driven.
The process has been shown to improve the quality of prehospital care and reduce variation in practice.
FAQ
What are the key steps involved in the National Prehospital Evidence-Based Guideline Model Process?
The key steps include identifying the need for a guideline, conducting a systematic review, developing draft recommendations, obtaining stakeholder consensus, and implementing and evaluating the guideline.
What is the role of systematic reviews in the process?
Systematic reviews provide a comprehensive and unbiased synthesis of the best available evidence on a specific topic. They help to identify the most effective interventions and inform the development of evidence-based guidelines.
How does the process ensure stakeholder engagement and consensus-building?
The process involves a multidisciplinary group of stakeholders, including clinicians, researchers, policymakers, and patient representatives. Their input and consensus are essential for developing guidelines that are both scientifically sound and practically applicable.